12. Examination of VTP modes
VTP as Vlan trunking protocol make management of VLAN database across network simply but is proprietary. VTP allows configure appropriate VLANs on one switch (VTP server) and then propagate these VLANs to whole network (Other VTP server with lover revision number or other VTP clients).
But be careful when adding preconfigured switch – higher revision number take precedents and will populate preconfigured VLANs to entire network. Possibly best thing that you can du is change VTP domain name to another and then to expected because change in VTP domain name reset revision number to zero. Higher revision number mean „I have more accurate information about what is in network expected to do“.
Benefits of use VTP are:
- consistency in VLAN across network
- dynamic trunk configuration when VLANs are introduced to network
In VTP terminology we must concern with these terms
- VTP domain – one or more interconnecting switch same VLAN configured. L3 devices dictate domain boundary.
- VTP advertisements – distribute and synchronize VLANs
- VTP modes – defines interaction with spread advertisements of VTP protocol across network
- VTP pruning – restrict flooding traffic to switches where are not appropriate VLANs. Help save available bandwidth on network trunks.
VTP modes are:
- VTP Server (default mode) – advertise VTP domain VLAN information to other enabled SW in same VTP domain (store VLAN info in NVRAM!!!). From server can be VLAN created, renamed or deleted.
- VTP client – only stores VLAN info. Is not default – vtp mode client CLI command must be configured. can not any way change configured VLANs as server mode can, but accept server made changes (exception is higher revision number that can harm whole network – please before adding used switch to existing network reset revision number!!!!).
- VTP transparent – forward VTP advertisement but do not participate on VTP.
Now we can take closer look at our training lab. Preconfigured scenario can be obtained from here (PKT 5.2 or above).
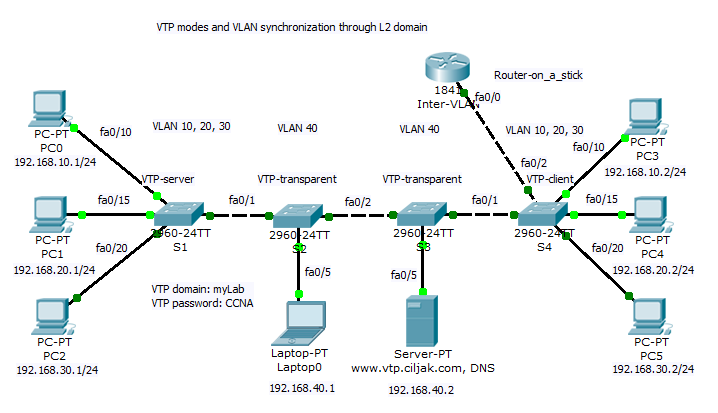
All switches participate on same VTP domain with name: myLab (please remember that names are case sensitive!!!). Switch S1 act as VTP server and can introduce and change VLAN to network. S4 is client switch that will accept VLANs modified by VTP server S1. Storage and administrative devices are connected to two switches S2 and S3. These are VTP transparent and contain only private VLAN 40 but trunk link between S1-S2-S3-S4-Inter VLAN router must be allowed for all VLAN (is default but show interface trunk and per trunk configured switchport trunk allowed vlan nr.nr, .. can help correct errors wen occur.).
Inter VLAN communication (reachability is enabled by router on a stick Inter VLAN router. If some access are expected be prohibited (access from clients to administrative VLAN with other ports as 80 and 443or 53 then appropriate access list must be created and assigned on appropriate interface to take effect.)
Now we can examine our topology:
- Status of VTP enabled protocol on S1 is displayed after typing command show vtp status under privileged exec mode or after do under other config modes
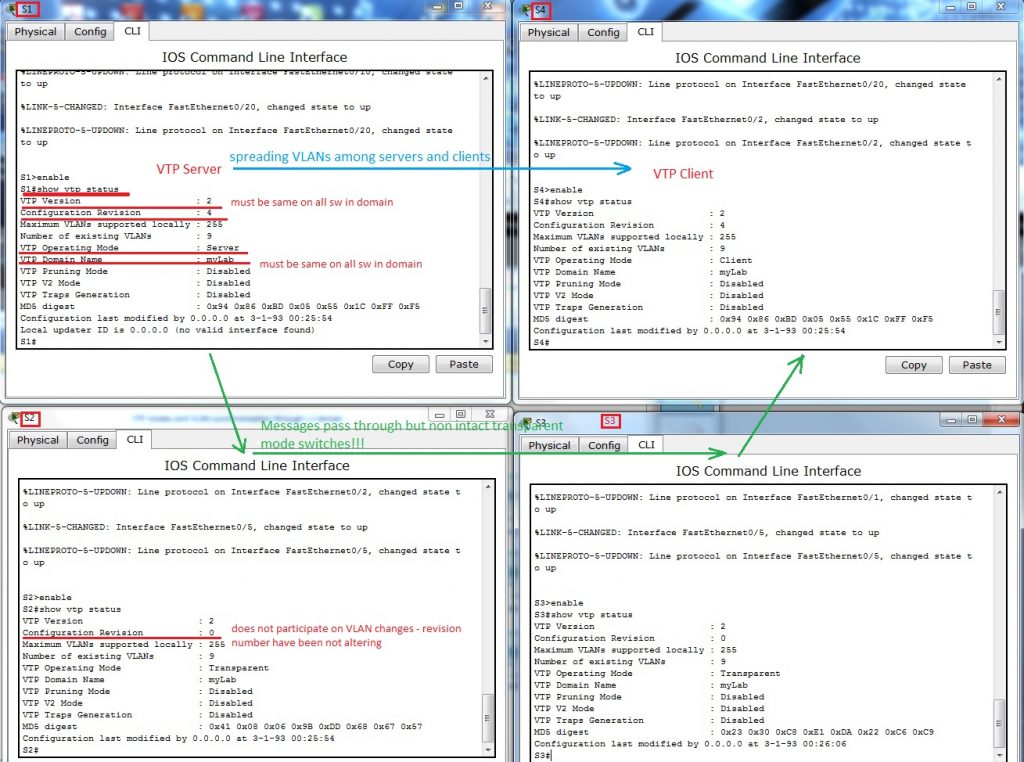
- VLANs spread from S1 to S4 does not alter config on S3 and S2 in transparent mode.
- Examination of allowed VLANs on trunk link among switches – show interface trunk
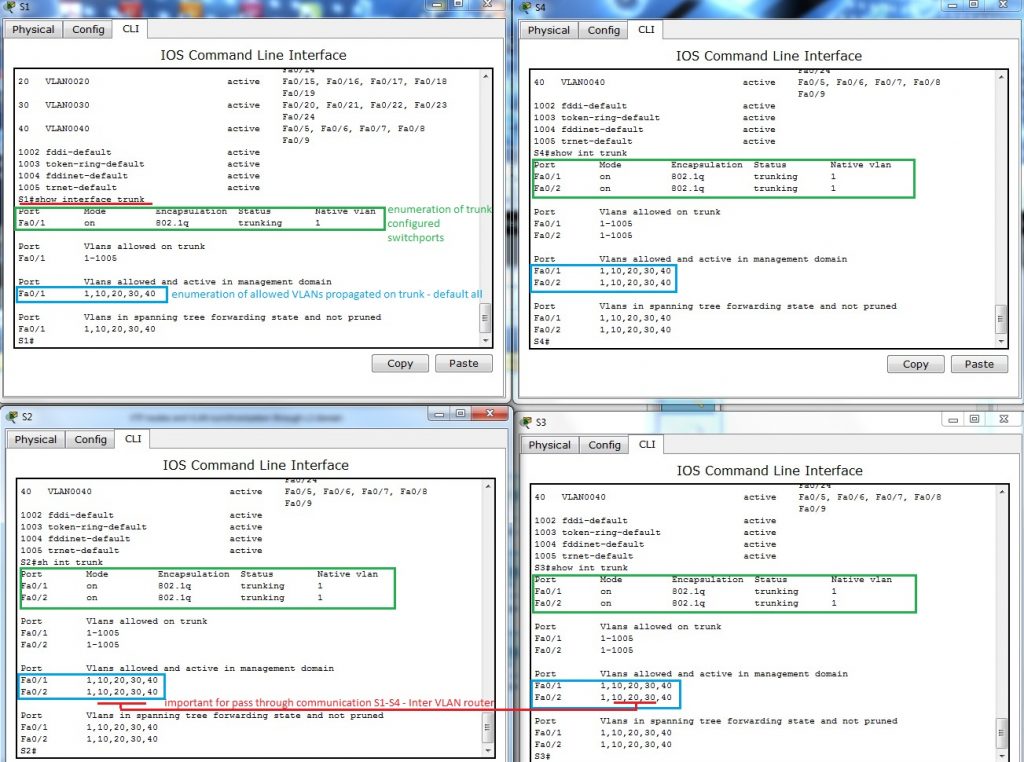
Because default are allowed all VLANs to propagate across trunk, no additional commands are necessary – but keep in mind that they must be allowed or somebody for security reasons can enable only appropriate VLANs.
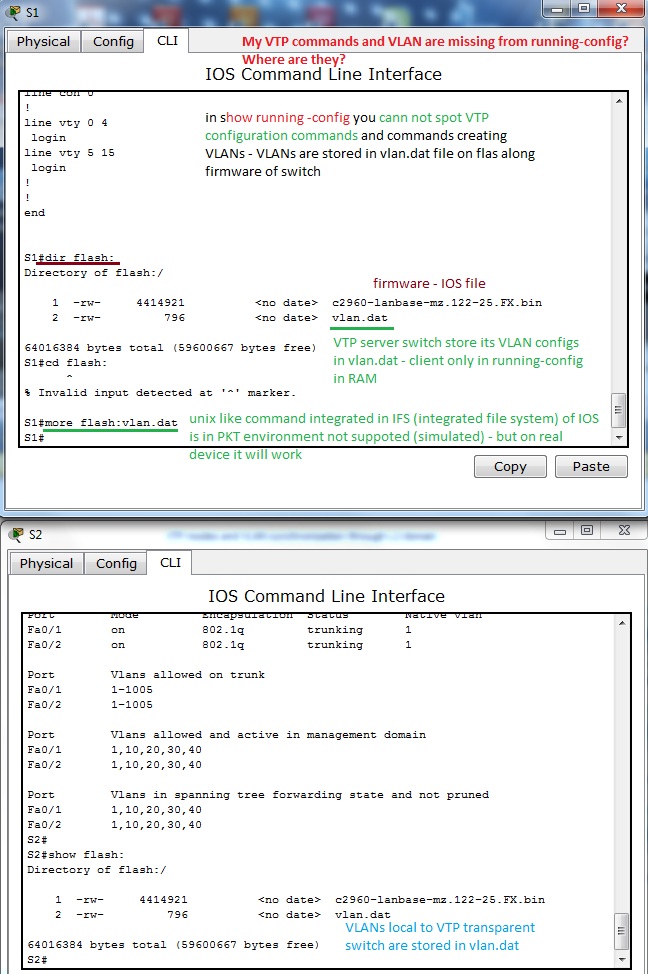
4. A bit confusing output from show running-config. You would by surprised where are all VTP config commands and VLANs that you created. But no worry, they are stored in vlan.dat in router flash. Vtp config can be examined with earlier mentioned commands. But next figure will explain something that you can be interested in.
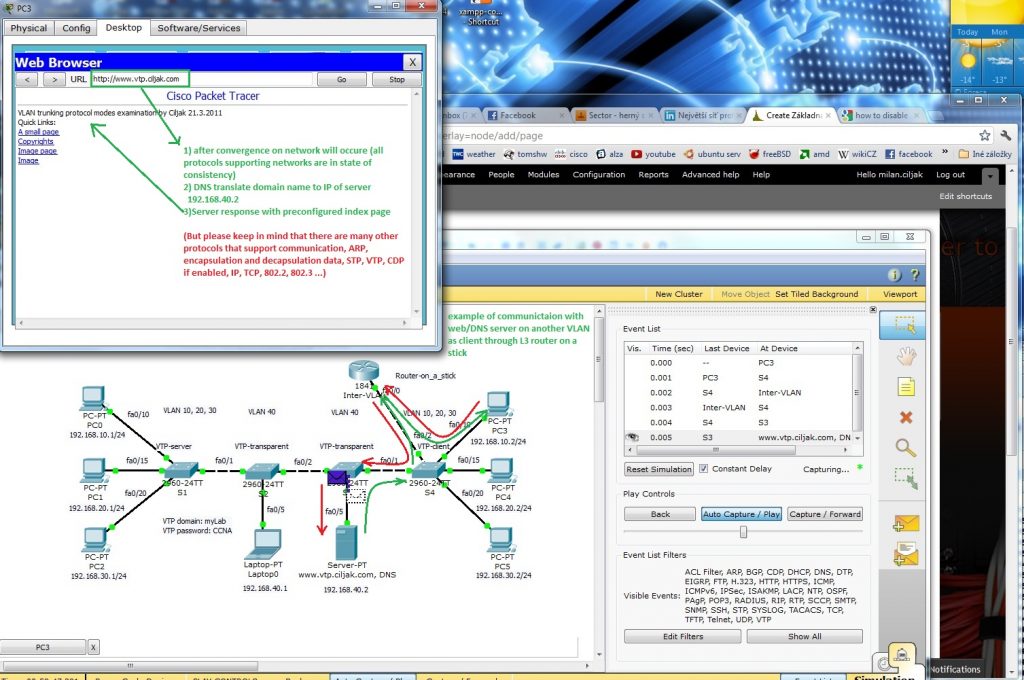
5. Example of real message exchange in training environment – web access. When there are devices on different VLANs they must communicate through L3 device (L3 traditional routing scenario, Router on a stick or introducing SVI interfaces on L3 capable switch). Now it is important feel all protocols that support exchange of messages through our network – HTTP, DNS, TCP, IP, 802.2 LLC, 802.3 Ethernet, ARP, routing protocols if needed, VTP, STP, CDP (on cisco network but all managed network use something), SNMP for management … and many many others. That all lies beneath network exchange of our communication (ICQ, e-mail, facebook, youtube, skype, VoIP …).